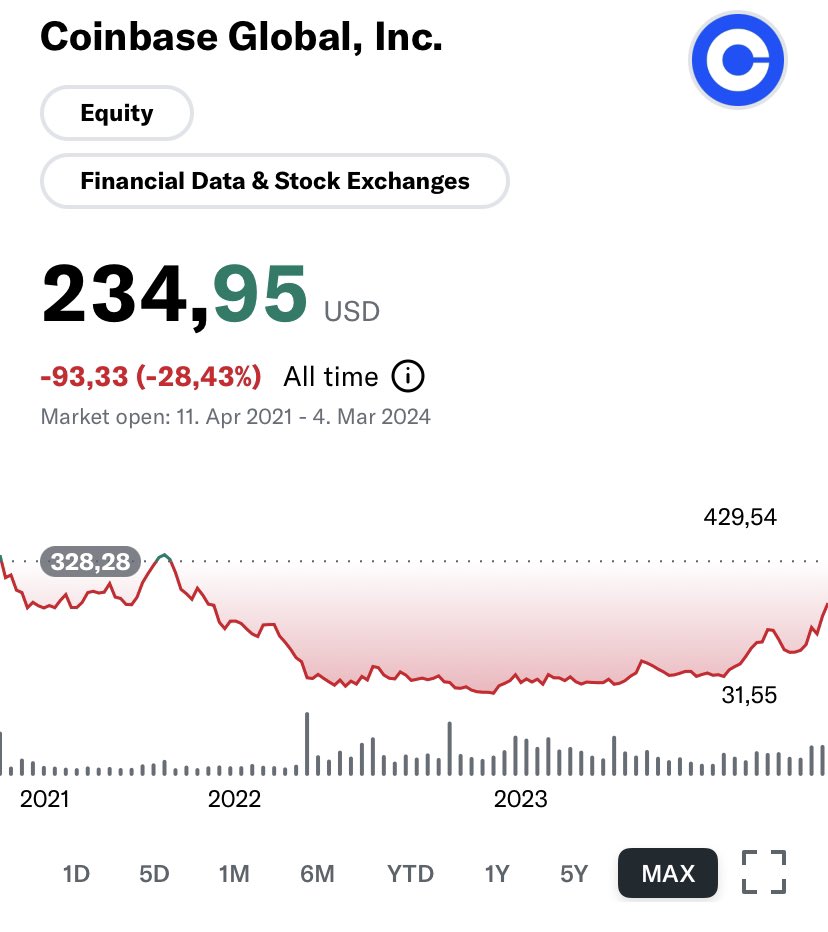
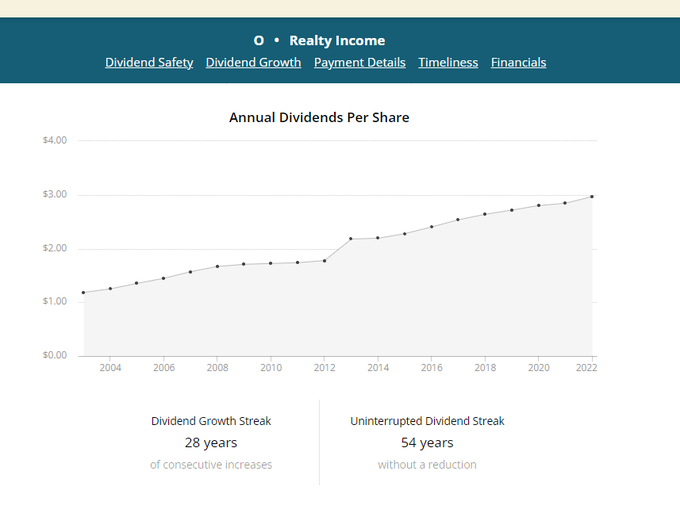
While the main benefits of dual-class structures often revolve around founder control and long-term focus, there are indeed other potential advantages to consider:
Increased Efficiency in Decision-Making: With a smaller group holding significant voting power, decision-making processes can be faster and more streamlined. This can be particularly advantageous for startups and agile companies needing to adapt quickly to market changes.
Attract Investors with Different Risk Appetites: Dual-class structures can attract two distinct types of investors: those seeking higher voting power and control alongside potentially higher risks, and those who prioritize lower voting power but potentially more stable and predictable returns. This diversification can benefit the company by bringing in a wider range of capital and expertise.
Enhanced Focus on Innovation: As founders and management hold more control, they can direct resources towards long-term innovative projects that may not immediately yield profits, potentially leading to breakthroughs and competitive advantages in the future.
Protection Against Activist Investors: The entrenched control by founders can offer a shield against short-termist activist investors who might push for decisions that prioritize immediate financial gains over long-term value creation.
Improved Shareholder Alignment: If super-voting shares are distributed strategically to key executives and senior leadership, their interests become more closely aligned with those of the overall shareholder base, potentially leading to better decision-making in the long run.
Global Competitiveness: Dual-class structures are more common in certain countries like the US and China, where public markets might be less forgiving of long-term investment strategies. This can give companies from these regions a competitive edge when facing companies from jurisdictions with a stricter one-share-one-vote approach.
However, it’s crucial to remember that these potential benefits are not guaranteed and depend on various factors like the specific design of the dual-class structure, the company’s governance practices, and the overall market context. As with any business decision, weighing the potential benefits and drawbacks with careful consideration is key before implementing a dual-class structure.